Channel App Auth Flow
If your application requires authentication to access resources and you want to leverage the existing user ecosystem within Mezon communities, Channel App provides an advanced feature for developers to integrate authentication and authorization of channel users through Mezon's user system.
Channel App offers a powerful authentication mechanism that allows seamless integration between your web application and Mezon's user base, eliminating the need for separate user management systems.
What is Hash-Based Authentication?
Hash-based authentication is a secure method where:
- User authentication data is embedded in a cryptographically signed hash string by the Mezon platform
- The hash contains user information and is validated using HMAC-SHA256 signatures
- Your web application validates the hash signature to authenticate users
- No external OAuth2 redirects are required
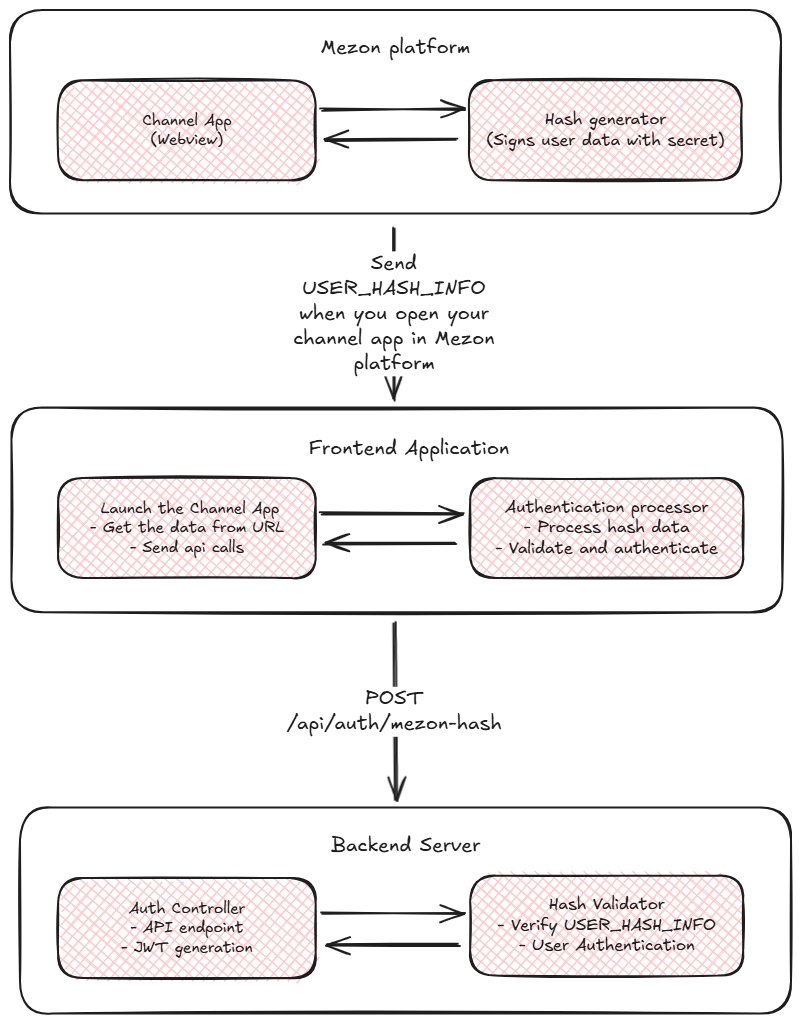
Architecture Overview
By following the Getting Started Guide, you now have a channel app on the Mezon platform with your web application integrated. Let's explore the relationship between the different components in the authentication flow.
Hash Data Structure
The hash data received from Mezon contains the following components:
Raw Hash Format
query_id=AAHdF6UqAAAAAB0XpSoKhRAd&user=%7B%22id%22%3A123456789%2C%22username%22%3A%22mezon_dev%22%2C%22mezon_id%22%3A%22mezon.dev%40ncc.asia%22%7D&auth_date=1640995200&signature=abc123def456&hash=7f3c4e8a9b2d1f6e5c8a7b4e9d2f8c1e6a9b3c7d
Decoded Parameters
query_id: Unique query identifier from Mezonuser: URL-encoded JSON string containing user informationauth_date: Unix timestamp of when the authentication was createdsignature: Additional signature data for verificationhash: HMAC-SHA256 signature of all the data (used for validation)
User Object Structure
{
"id": 123456789,
"username": "mezon_dev",
"display_name": "Mezon Dev",
"avatar_url": "https://cdn.mezon.ai/avatar.jpg",
"mezon_id": "mezon.dev@ncc.asia"
}
How to Implement Hash Authentication Flow?
Step 1: Frontend Implementation
When Mezon opens your channel app, it passes user authentication data via the URL query parameter. Extract this data and send it to your backend for validation.
Extract Authentication Data from URL
// Extract authentication data from URL query parameters
function getAuthDataFromURL() {
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
const authData = urlParams.get('data');
if (!authData) {
console.warn('No authentication data found in URL');
return null;
}
// Decode the URL-encoded data
return decodeURIComponent(authData);
}
// Get the authentication data
const rawHashData = getAuthDataFromURL();
if (rawHashData) {
console.log('Authentication data received:', rawHashData);
// Process the hash data for authentication
authenticateWithHash(rawHashData);
} else {
console.error('No authentication data available');
// Handle the case where no auth data is present
}
Complete Frontend Implementation
Here's a comprehensive HTML and JavaScript implementation for handling Mezon authentication via URL parameters:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Mezon Channel App Authentication</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
background: var(--mezon-bg-color, #f5f5f5);
color: var(--mezon-text-color, #333);
}
.auth-container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background: var(--mezon-card-bg, #ffffff);
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.status {
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin: 10px 0;
}
.status.loading {
background-color: #fff3cd;
color: #856404;
}
.status.success {
background-color: #d4edda;
color: #155724;
}
.status.error {
background-color: #f8d7da;
color: #721c24;
}
.status.info {
background-color: #d1ecf1;
color: #0c5460;
}
.auth-details {
background: #f8f9fa;
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin: 15px 0;
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 12px;
white-space: pre-wrap;
}
button {
background: var(--mezon-button-bg, #007bff);
color: var(--mezon-button-text, white);
border: none;
padding: 10px 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
margin: 5px;
}
button:hover {
background: var(--mezon-button-hover, #0056b3);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="auth-container">
<h1>Mezon Channel App Authentication</h1>
<div id="connectionStatus" class="status info">Initializing...</div>
<div id="authSection">
<h3>Authentication Status</h3>
<div id="authStatus" class="status info">Ready to authenticate</div>
</div>
<div id="userInfo" style="display: none;">
<h3>Authenticated User</h3>
<div id="userDetails" class="auth-details"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
class MezonAuthApp {
constructor() {
this.authEndpoint = "/api/auth/mezon-hash"; // Your backend auth endpoint
this.init();
}
init() {
this.updateConnectionStatus();
this.checkForAuthData();
}
updateConnectionStatus() {
const statusEl = document.getElementById("connectionStatus");
statusEl.className = "status success";
statusEl.innerHTML = "✅ Channel App Loaded";
}
checkForAuthData() {
// Extract authentication data from URL
const authData = this.getAuthDataFromURL();
if (authData) {
this.updateAuthStatus("Authentication data found", "info");
this.authenticateWithHash(authData);
} else {
this.updateAuthStatus("No authentication data found in URL", "info");
}
}
getAuthDataFromURL() {
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
const authData = urlParams.get('data');
if (!authData) {
console.warn('No authentication data found in URL');
return null;
}
try {
// Decode the URL-encoded data
const decodedData = decodeURIComponent(authData);
console.log('Authentication data received');
return decodedData;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error decoding authentication data:', error);
return null;
}
}
authenticateWithHash(rawHashData) {
console.log("Processing hash data for authentication");
this.updateAuthStatus("Processing authentication...", "loading");
try {
// Process hash data
const authModel = this.processHashData(rawHashData);
// Send to backend for validation
this.sendAuthRequest(authModel);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error processing hash data:", error);
this.updateAuthStatus(
"Error processing authentication data",
"error"
);
}
}
processHashData(rawHashData) {
// Base64 encode the hash data for secure transmission
const encodedHashData = btoa(rawHashData);
return {
hashData: encodedHashData,
};
}
async sendAuthRequest(authModel) {
try {
const response = await fetch(this.authEndpoint, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(authModel),
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Authentication failed: ${response.statusText}`);
}
const result = await response.json();
this.handleAuthSuccess(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Authentication request failed:", error);
this.updateAuthStatus(
`Authentication failed: ${error.message}`,
"error"
);
}
}
handleAuthSuccess(result) {
console.log("Authentication successful:", result);
this.updateAuthStatus("Authentication successful!", "success");
// Store the authentication token
if (result.token) {
localStorage.setItem("auth_token", result.token);
}
// Display user information
if (result.user) {
this.displayUserInfo(result.user);
}
// Redirect or continue with app initialization
// window.location.href = '/dashboard';
}
displayUserInfo(user) {
const userInfoDiv = document.getElementById("userInfo");
const userDetailsDiv = document.getElementById("userDetails");
userDetailsDiv.textContent = JSON.stringify(user, null, 2);
userInfoDiv.style.display = "block";
}
updateAuthStatus(message, type) {
const authStatusEl = document.getElementById("authStatus");
authStatusEl.className = `status ${type}`;
authStatusEl.textContent = message;
}
}
// Initialize the app when DOM is ready
const mezonAuthApp = new MezonAuthApp();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Simplified Authentication Handler
For integration into existing applications, here's a simplified JavaScript class:
class SimpleMezonAuth {
constructor(options = {}) {
this.authEndpoint = options.authEndpoint || "/api/auth/mezon-hash";
this.onSuccess = options.onSuccess || this.defaultSuccessHandler;
this.onError = options.onError || this.defaultErrorHandler;
this.init();
}
init() {
this.startAuthFlow();
}
startAuthFlow() {
// Extract auth data from URL
const authData = this.getAuthDataFromURL();
if (authData) {
this.processAuthentication(authData);
} else {
this.onError('No authentication data found in URL');
}
}
getAuthDataFromURL() {
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search);
const authData = urlParams.get('data');
if (!authData) {
return null;
}
try {
return decodeURIComponent(authData);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error decoding auth data:', error);
return null;
}
}
async processAuthentication(rawHashData) {
try {
const authData = {
hashData: btoa(rawHashData),
};
const response = await fetch(this.authEndpoint, {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify(authData),
});
const result = await response.json();
if (result.success) {
this.onSuccess(result);
} else {
this.onError(result.error);
}
} catch (error) {
this.onError(error.message);
}
}
defaultSuccessHandler(result) {
console.log("Authentication successful:", result);
if (result.token) {
localStorage.setItem("auth_token", result.token);
}
}
defaultErrorHandler(error) {
console.error("Authentication failed:", error);
}
}
// Usage example:
// const auth = new SimpleMezonAuth({
// authEndpoint: '/api/auth/mezon-hash',
// onSuccess: (result) => {
// console.log('User authenticated:', result.user);
// window.location.href = '/dashboard';
// },
// onError: (error) => {
// alert('Authentication failed: ' + error);
// }
// });
Step 2: Backend Implementation
On your server side, you need to define an endpoint that accepts the user hash information and validates it.
Hash Validation Process
The hash validation process involves understanding the mechanism and data that Mezon uses. The hash token creation process includes 3 steps:
- MD5 Hash: Your App Secret is hashed using MD5, the result is used as the key for step 2
- HMAC-SHA256: Use HMAC-SHA256 with the key from step 1 to hash the string "WebAppData", the result is used in step 3
- Final Hash: Use all data sent from the frontend (except the hash part) as input for step 3, combined with the result from step 2 as the key. Hash all data using HMAC-SHA256 to get the final hash string
- Node.js
- Python
- Go
- Java
- C#
const crypto = require('crypto');
function validateMezonHash(appSecret, hashData) {
try {
// Parse hash data
const delimiter = '&hash=';
const index = hashData.indexOf(delimiter);
const queryData = hashData.substring(0, index);
const receivedHash = hashData.substring(index + delimiter.length);
// Step 1: MD5 hash of app secret
const hashedSecret = crypto.createHash('md5').update(appSecret).digest('hex');
// Step 2: HMAC-SHA256 of "WebAppData" with hashed secret
const secretKey = crypto.createHmac('sha256', hashedSecret).update('WebAppData').digest();
// Step 3: HMAC-SHA256 of query data with secret key
const computedHash = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secretKey).update(queryData).digest('hex');
// Compare hashes
return computedHash === receivedHash;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Hash validation error:', error);
return false;
}
}
// Usage example
app.post('/api/auth/mezon-hash', (req, res) => {
const { hashData } = req.body;
const rawHashData = Buffer.from(hashData, 'base64').toString('utf-8');
const isValid = validateMezonHash(process.env.MEZON_APP_SECRET, rawHashData);
if (isValid) {
// Extract user data and create session
const userData = parseUserData(rawHashData);
const token = generateJWTToken(userData);
res.json({
success: true,
accessToken: token,
user: userData
});
} else {
res.status(401).json({
success: false,
error: 'Invalid hash signature'
});
}
});
import hmac
import hashlib
import base64
import urllib.parse
import json
def validate_mezon_hash(app_secret, hash_data):
try:
# Parse hash data
delimiter = '&hash='
index = hash_data.find(delimiter)
query_data = hash_data[:index]
received_hash = hash_data[index + len(delimiter):]
# Step 1: MD5 hash of app secret
hashed_secret = hashlib.md5(app_secret.encode()).hexdigest()
# Step 2: HMAC-SHA256 of "WebAppData" with hashed secret
secret_key = hmac.new(
hashed_secret.encode(),
b'WebAppData',
hashlib.sha256
).digest()
# Step 3: HMAC-SHA256 of query data with secret key
computed_hash = hmac.new(
secret_key,
query_data.encode(),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
# Compare hashes
return computed_hash == received_hash
except Exception as e:
print(f"Hash validation error: {e}")
return False
def parse_user_data(hash_data):
# Extract query parameters
delimiter = '&hash='
query_data = hash_data[:hash_data.find(delimiter)]
params = urllib.parse.parse_qs(query_data)
# Parse user JSON
user_json = urllib.parse.unquote(params['user'][0])
user_data = json.loads(user_json)
return {
'query_id': params['query_id'][0],
'user': user_data,
'auth_date': int(params['auth_date'][0]),
'signature': params['signature'][0] if 'signature' in params else None
}
# Flask example
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import jwt
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/auth/mezon-hash', methods=['POST'])
def mezon_hash_auth():
data = request.get_json()
hash_data = data.get('hashData')
# Decode base64 hash data
raw_hash_data = base64.b64decode(hash_data).decode('utf-8')
# Validate hash
app_secret = os.getenv('MEZON_APP_SECRET')
is_valid = validate_mezon_hash(app_secret, raw_hash_data)
if is_valid:
# Parse user data
user_data = parse_user_data(raw_hash_data)
# Generate JWT token
token = jwt.encode({
'user_id': user_data['user']['id'],
'username': user_data['user']['username'],
'mezon_id': user_data['user']['mezon_id']
}, os.getenv('JWT_SECRET'), algorithm='HS256')
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'accessToken': token,
'user': user_data['user']
})
else:
return jsonify({
'success': False,
'error': 'Invalid hash signature'
}), 401
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/md5"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/hex"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"net/url"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type MezonUser struct {
ID int64 `json:"id"`
Username string `json:"username"`
MezonID string `json:"mezon_id"`
}
type HashData struct {
QueryID string `json:"query_id"`
User MezonUser `json:"user"`
AuthDate int64 `json:"auth_date"`
Signature string `json:"signature"`
}
func validateMezonHash(appSecret, hashData string) bool {
// Parse hash data
delimiter := "&hash="
index := strings.Index(hashData, delimiter)
if index == -1 {
return false
}
queryData := hashData[:index]
receivedHash := hashData[index+len(delimiter):]
// Step 1: MD5 hash of app secret
hasher := md5.New()
hasher.Write([]byte(appSecret))
hashedSecret := hex.EncodeToString(hasher.Sum(nil))
// Step 2: HMAC-SHA256 of "WebAppData" with hashed secret
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(hashedSecret))
mac.Write([]byte("WebAppData"))
secretKey := mac.Sum(nil)
// Step 3: HMAC-SHA256 of query data with secret key
mac2 := hmac.New(sha256.New, secretKey)
mac2.Write([]byte(queryData))
computedHash := hex.EncodeToString(mac2.Sum(nil))
// Compare hashes
return computedHash == receivedHash
}
func parseUserData(hashData string) (*HashData, error) {
delimiter := "&hash="
index := strings.Index(hashData, delimiter)
queryData := hashData[:index]
// Parse query parameters
values, err := url.ParseQuery(queryData)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Parse user JSON
userJSON, err := url.QueryUnescape(values.Get("user"))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var user MezonUser
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(userJSON), &user); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
authDate, err := strconv.ParseInt(values.Get("auth_date"), 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &HashData{
QueryID: values.Get("query_id"),
User: user,
AuthDate: authDate,
Signature: values.Get("signature"),
}, nil
}
func mezonHashAuthHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var reqData struct {
HashData string `json:"hashData"`
}
if err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&reqData); err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Invalid request", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// Decode base64 hash data
rawHashData, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(reqData.HashData)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Invalid hash data", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// Validate hash
appSecret := os.Getenv("MEZON_APP_SECRET")
if !validateMezonHash(appSecret, string(rawHashData)) {
http.Error(w, "Invalid hash signature", http.StatusUnauthorized)
return
}
// Parse user data
userData, err := parseUserData(string(rawHashData))
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Failed to parse user data", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// Generate JWT token (implement your JWT logic here)
token := generateJWTToken(userData.User)
response := map[string]interface{}{
"success": true,
"accessToken": token,
"user": userData.User,
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class MezonHashValidator {
public static boolean validateMezonHash(String appSecret, String hashData) {
try {
// Parse hash data
String delimiter = "&hash=";
int index = hashData.indexOf(delimiter);
if (index == -1) return false;
String queryData = hashData.substring(0, index);
String receivedHash = hashData.substring(index + delimiter.length());
// Step 1: MD5 hash of app secret
MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] hashedSecretBytes = md5.digest(appSecret.getBytes());
String hashedSecret = bytesToHex(hashedSecretBytes);
// Step 2: HMAC-SHA256 of "WebAppData" with hashed secret
Mac mac1 = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec1 = new SecretKeySpec(hashedSecret.getBytes(), "HmacSHA256");
mac1.init(secretKeySpec1);
byte[] secretKey = mac1.doFinal("WebAppData".getBytes());
// Step 3: HMAC-SHA256 of query data with secret key
Mac mac2 = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec2 = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey, "HmacSHA256");
mac2.init(secretKeySpec2);
byte[] computedHashBytes = mac2.doFinal(queryData.getBytes());
String computedHash = bytesToHex(computedHashBytes);
// Compare hashes
return computedHash.equals(receivedHash);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
result.append(String.format("%02x", b));
}
return result.toString();
}
public static Map<String, Object> parseUserData(String hashData) throws Exception {
String delimiter = "&hash=";
int index = hashData.indexOf(delimiter);
String queryData = hashData.substring(0, index);
// Parse query parameters
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>();
String[] pairs = queryData.split("&");
for (String pair : pairs) {
String[] keyValue = pair.split("=", 2);
if (keyValue.length == 2) {
params.put(keyValue[0], URLDecoder.decode(keyValue[1], "UTF-8"));
}
}
// Parse user JSON
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Map<String, Object> user = mapper.readValue(params.get("user"), Map.class);
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("query_id", params.get("query_id"));
result.put("user", user);
result.put("auth_date", Long.parseLong(params.get("auth_date")));
result.put("signature", params.get("signature"));
return result;
}
// Spring Boot Controller example
@RestController
public class AuthController {
@Value("${mezon.app.secret}")
private String appSecret;
@PostMapping("/api/auth/mezon-hash")
public ResponseEntity<?> mezonHashAuth(@RequestBody Map<String, String> request) {
try {
String hashData = request.get("hashData");
// Decode base64 hash data
byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(hashData);
String rawHashData = new String(decodedBytes);
// Validate hash
if (!validateMezonHash(appSecret, rawHashData)) {
return ResponseEntity.status(401).body(
Map.of("success", false, "error", "Invalid hash signature")
);
}
// Parse user data
Map<String, Object> userData = parseUserData(rawHashData);
// Generate JWT token
String token = generateJWTToken(userData);
return ResponseEntity.ok(Map.of(
"success", true,
"accessToken", token,
"user", userData.get("user")
));
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(500).body(
Map.of("success", false, "error", "Authentication failed")
);
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
public class MezonHashValidator
{
public static bool ValidateMezonHash(string appSecret, string hashData)
{
try
{
// Parse hash data
string delimiter = "&hash=";
int index = hashData.IndexOf(delimiter);
if (index == -1) return false;
string queryData = hashData.Substring(0, index);
string receivedHash = hashData.Substring(index + delimiter.Length);
// Step 1: MD5 hash of app secret
using (var md5 = MD5.Create())
{
byte[] hashedSecretBytes = md5.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(appSecret));
string hashedSecret = BitConverter.ToString(hashedSecretBytes)
.Replace("-", "").ToLowerInvariant();
// Step 2: HMAC-SHA256 of "WebAppData" with hashed secret
using (var hmac1 = new HMACSHA256(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(hashedSecret)))
{
byte[] secretKey = hmac1.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("WebAppData"));
// Step 3: HMAC-SHA256 of query data with secret key
using (var hmac2 = new HMACSHA256(secretKey))
{
byte[] computedHashBytes = hmac2.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(queryData));
string computedHash = BitConverter.ToString(computedHashBytes)
.Replace("-", "").ToLowerInvariant();
// Compare hashes
return computedHash.Equals(receivedHash, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hash validation error: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
public static Dictionary<string, object> ParseUserData(string hashData)
{
string delimiter = "&hash=";
int index = hashData.IndexOf(delimiter);
string queryData = hashData.Substring(0, index);
// Parse query parameters
var queryParams = HttpUtility.ParseQueryString(queryData);
// Parse user JSON
string userJson = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(queryParams["user"]);
var user = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Dictionary<string, object>>(userJson);
return new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["query_id"] = queryParams["query_id"],
["user"] = user,
["auth_date"] = long.Parse(queryParams["auth_date"]),
["signature"] = queryParams["signature"]
};
}
}
// ASP.NET Core Controller example
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class AuthController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
public AuthController(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_configuration = configuration;
}
[HttpPost("mezon-hash")]
public IActionResult MezonHashAuth([FromBody] MezonHashAuthRequest request)
{
try
{
// Decode base64 hash data
string rawHashData = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(request.HashData));
// Validate hash
string appSecret = _configuration["Mezon:AppSecret"];
if (!MezonHashValidator.ValidateMezonHash(appSecret, rawHashData))
{
return Unauthorized(new { success = false, error = "Invalid hash signature" });
}
// Parse user data
var userData = MezonHashValidator.ParseUserData(rawHashData);
// Generate JWT token
string token = GenerateJWTToken(userData);
return Ok(new
{
success = true,
accessToken = token,
user = userData["user"]
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(500, new { success = false, error = "Authentication failed" });
}
}
}
public class MezonHashAuthRequest
{
public string HashData { get; set; }
}
Complete Backend Implementation Example (Node.js/Express)
const express = require("express");
const crypto = require("crypto");
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
// Utility functions
function validateMezonHash(appSecret, hashData) {
try {
const delimiter = "&hash=";
const index = hashData.indexOf(delimiter);
const queryData = hashData.substring(0, index);
const receivedHash = hashData.substring(index + delimiter.length);
// Hash validation process
const hashedSecret = crypto
.createHash("md5")
.update(appSecret)
.digest("hex");
const secretKey = crypto
.createHmac("sha256", hashedSecret)
.update("WebAppData")
.digest();
const computedHash = crypto
.createHmac("sha256", secretKey)
.update(queryData)
.digest("hex");
return computedHash === receivedHash;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Hash validation error:", error);
return false;
}
}
function parseUserData(hashData) {
const delimiter = "&hash=";
const queryData = hashData.substring(0, hashData.indexOf(delimiter));
const params = new URLSearchParams(queryData);
const userJSON = decodeURIComponent(params.get("user"));
const user = JSON.parse(userJSON);
return {
query_id: params.get("query_id"),
user: user,
auth_date: parseInt(params.get("auth_date")),
signature: params.get("signature"),
};
}
function generateJWTToken(userData) {
const payload = {
user_id: userData.user.id,
username: userData.user.username,
mezon_id: userData.user.mezon_id,
exp: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + 60 * 60 * 24, // 24 hours
};
return jwt.sign(payload, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
}
// Authentication endpoint
app.post("/api/auth/mezon-hash", async (req, res) => {
try {
const { hashData } = req.body;
if (!hashData) {
return res.status(400).json({
success: false,
error: "Hash data is required",
});
}
// Decode base64 hash data
const rawHashData = Buffer.from(hashData, "base64").toString("utf-8");
console.log("Received hash data:", rawHashData);
// Validate hash signature
const isValid = validateMezonHash(
process.env.MEZON_APP_SECRET,
rawHashData
);
if (!isValid) {
return res.status(401).json({
success: false,
error: "Invalid hash signature",
});
}
// Parse user data
const userData = parseUserData(rawHashData);
console.log("Parsed user data:", userData);
// Check if user exists in your database
const user = await findOrCreateUser(userData.user);
if (!user) {
return res.status(401).json({
success: false,
error: "User not found or cannot be created",
});
}
// Generate JWT token
const accessToken = generateJWTToken(userData);
// Return successful authentication
res.json({
success: true,
accessToken: accessToken,
expiresIn: 86400, // 24 hours in seconds
user: {
id: user.id,
username: user.username,
email: user.email,
displayName: user.displayName,
},
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("Authentication error:", error);
res.status(500).json({
success: false,
error: "Internal server error",
});
}
});
// Mock user database operations
async function findOrCreateUser(mezonUser) {
// Implement your user lookup/creation logic here
// This could involve database queries to find existing users
// or create new users based on Mezon data
// Example implementation:
let user = await User.findOne({ email: mezonUser.mezon_id });
if (!user) {
// Create new user if doesn't exist
user = await User.create({
email: mezonUser.mezon_id,
username: mezonUser.username,
displayName: mezonUser.display_name || mezonUser.username,
avatarUrl: mezonUser.avatar_url,
mezonId: mezonUser.id,
});
}
return user;
}
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server running on port 3000");
});
Complete Authentication Flow
The complete flow works as follows:
- User opens channel app in Mezon
- Mezon generates hash with user data and cryptographic signature
- Mezon loads your web application with authentication data in URL query parameter (
?data=...) - Frontend extracts auth data: JavaScript reads the
dataparameter from URL - Data decoding: Frontend URL-decodes the authentication string
- Hash processing: Frontend base64 encodes hash and sends to backend
- Hash validation: Backend validates signature using cryptographic verification
- User authentication: Backend finds/creates user and generates JWT token
- Session establishment: Frontend stores token and redirects to application
Error Handling and Troubleshooting
Common Error Scenarios
Frontend Error Handling
// Comprehensive error handling in your service
public authenticateWithHash(authModel: MezonHashAuthModel): Observable<any> {
return this.http.post('/api/auth/mezon-hash', authModel).pipe(
map(response => ({ ...response, loading: false })),
catchError((error: HttpErrorResponse) => {
console.error('Authentication failed:', error);
let errorMessage = 'Authentication failed';
if (error.error?.error) {
errorMessage = error.error.error;
} else if (error.status === 401) {
errorMessage = 'Invalid authentication credentials';
} else if (error.status === 0) {
errorMessage = 'Network error - please check your connection';
}
return of({
loading: false,
success: false,
error: errorMessage
});
})
);
}
Backend Error Handling
app.post("/api/auth/mezon-hash", async (req, res) => {
try {
// ... authentication logic
} catch (error) {
console.error("Authentication error:", error);
// Return appropriate error responses
if (error.name === "ValidationError") {
return res.status(400).json({
success: false,
error: "Invalid request data",
});
} else if (error.name === "JsonWebTokenError") {
return res.status(500).json({
success: false,
error: "Token generation failed",
});
} else {
return res.status(500).json({
success: false,
error: "Internal server error",
});
}
}
});
Security Best Practices
- Always validate hash signatures before processing user data
- Use environment variables for sensitive configuration like app secrets
- Implement proper error handling without exposing internal details
- Add rate limiting to prevent abuse of authentication endpoints
- Log authentication attempts for security monitoring
- Validate user data before creating database records
- Use HTTPS for all communications in production
Testing Your Implementation
Backend Testing
// Test hash validation
const assert = require("assert");
function testHashValidation() {
const appSecret = "test-secret";
const validHashData =
"query_id=test&user=%7B%22id%22%3A123%7D&auth_date=1640995200&hash=valid-hash";
// Test with valid hash
const isValid = validateMezonHash(appSecret, validHashData);
console.log("Hash validation test:", isValid ? "PASSED" : "FAILED");
}
testHashValidation();
This completes the comprehensive Channel App Authentication Flow documentation. The hash-based authentication provides a secure and seamless way to authenticate users from Mezon into your application without requiring separate login flows.